"Powerledger was founded in 2016 to solve a pressing problem: Energy that comes from solar and wind is intermittent and lacks the steady quality that fossil fuels provide, and this causes problems for the grid."
Context & Opportunity
Powerledger is an Australia-origin clean energy software company founded in 2016 to address renewable intermittency and traceability by building agile, blockchain-enabled electricity markets. Its platform enables utilities, large corporates, and prosumers to track, trace, and trade every kilowatt-hour, supporting peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading, granular renewable energy certificates (RECs), and 24/7 carbon-free energy (CFE) procurement using time-stamped energy attribute certificates. The leadership philosophy centers on democratising energy participation, real-time settlement, and auditable provenance to accelerate decarbonisation while improving grid stability.
In India, national ambitions for 500 GW of non-fossil capacity by 2030 coincided with rapid growth in rooftop solar and distributed energy resources. At the same time, grid reliability challenges, under-utilised solar generation (especially in apartments with shared rooftops), limited smart meter penetration, and non-standardised solar metering created a need for flexible market infrastructure that could match local supply and demand, automate settlement, and visualise energy flows and CO2 intensity for ESG-grade reporting.
The Australia–India corridor gained momentum with AI-ECTA, which broadened openness to Australian innovation, catalysed business delegations, and encouraged collaboration between utilities, regulators, and technology providers. For a software-led market model like Powerledger’s, this corridor reduced barriers to pilot engagement and policy dialogue.
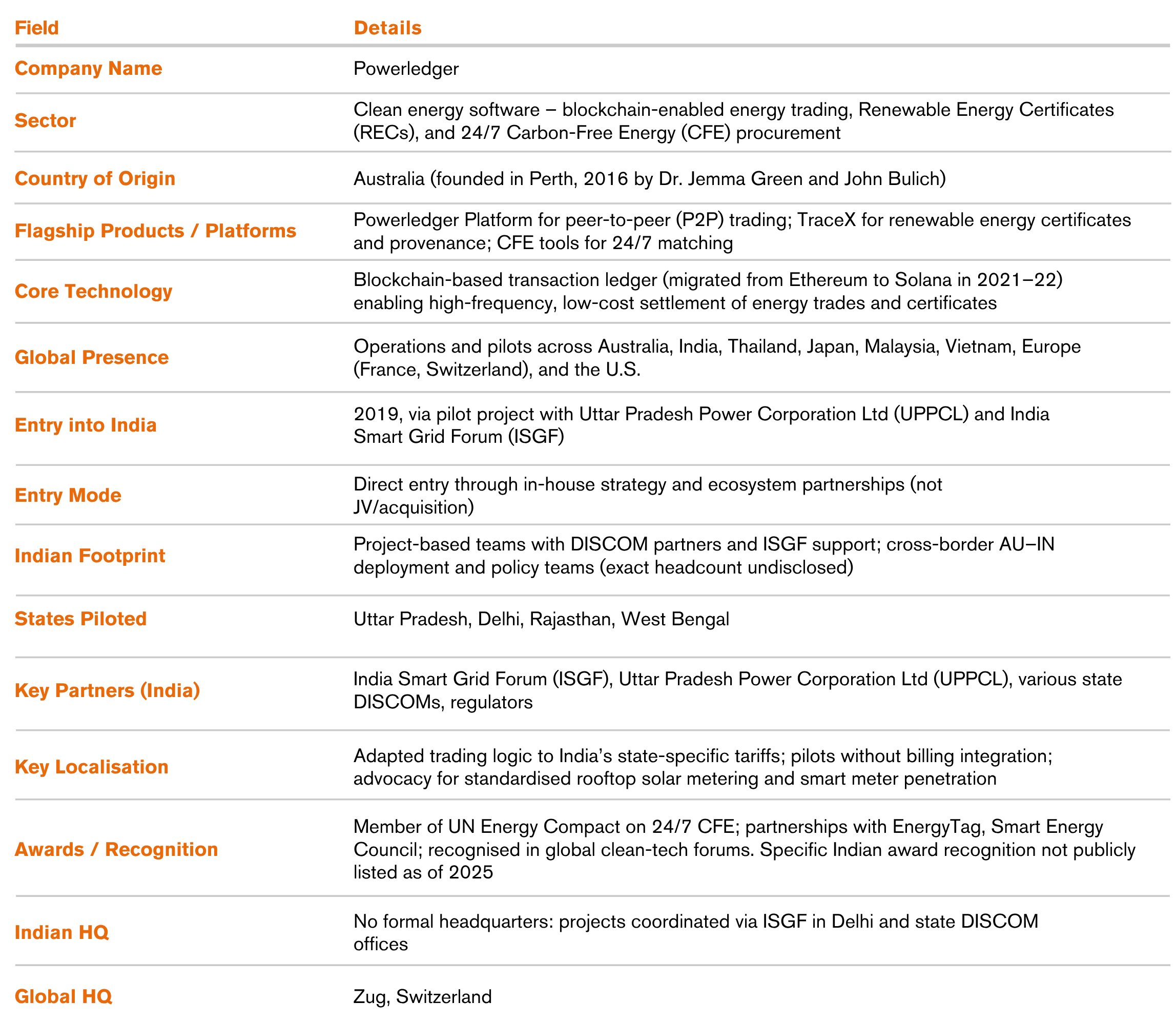
Entering India in 2019, starting with Uttar Pradesh and expanding pilots to Delhi, Rajasthan, and West Bengal, Powerledger aimed to progress from feasibility pilots to commercialisation, positioning blockchain as foundational market infrastructure for decentralised energy and granular certificates, and creating a replicable blueprint for other emerging markets.
India represented an inflection point that combined opportunity unlocking (new use-cases, partners, regulatory engagement) with capability scaling (high-throughput architecture and automation). Proving P2P trading and time-stamped certificates in one of the world’s most complex power systems would de-risk broader rollouts and accelerate the transition from pilots to state-by-state commercial deployment.

Strategy & Execution
In House Strategy
Powerledger entered India in 2019 via an in-house strategy that leveraged ecosystem partnerships rather than JV or acquisition. The company collaborated with the India Smart Grid Forum (ISGF), Uttar Pradesh Power Corporation Ltd (UPPCL), and other DISCOMs and regulators to conduct P2P pilots in states such as Uttar Pradesh, New Delhi, Rajasthan, and West Bengal. This partnership-led mode enabled rapid access to stakeholders, alignment with local priorities, and policy learning in live environments, minimising capital intensity while maximising regulatory engagement and technical validation in India’s grid context.
Recognising India’s state-driven power governance, Powerledger pursued a state-by-state approach, tailoring design, tariff handling (including tiered tariffs), and engagement to each regulatory setting. Pilots were designed to operate amid limited smart meter penetration, non-standardised rooftop solar metering, and shared rooftop constraints. The company prioritised trading logic, visibility of energy mix/CO2 intensity, and provenance while advocating investment in metering hardware as a prerequisite for live, commercial-scale trading. Education-first workshops, whitepapers, and regulator/utility collaboration drove awareness and trust in blockchain’s role in settlement and auditability. Messaging emphasised value for prosumers (utilising excess solar through local matching) and for DISCOMs (potential optimisation and alignment with decarbonisation objectives).
Powerledger’s platform uses blockchain for a secure, auditable, real-time transaction ledger, enabling smart contract-driven automation and granular energy provenance. This supports two-sided REC marketplaces and 24/7 CFE through time-stamped certificates that match consumption with green generation.Integration with Solana delivers speed and low transaction costs suitable for high-frequency micro-settlements expected at commercial scale, futureproofing for mass adoption. Tools that display energy generation and demand, energy mix, CO2 intensity, and source tracking support precise decarbonisation strategies and ESG reporting for enterprises and institutions.

Starting in Uttar Pradesh and expanding to Delhi, Rajasthan, and West Bengal, pilots focused on enabling trading without DISCOM billing integration, an intentional sequence to avoid regulatory bottlenecks while generating evidence for policy change and commercial enablement. The India strategy was designed by the in-house team, with ISGF as a pivotal collaborator to assess market readiness, convene stakeholders, and accelerate regulatory engagement through joint outputs like whitepapers.Core KPIs included participant numbers, energy traded, enrolled renewable capacity, and indicative savings for participants and DISCOMs. These metrics informed product iterations, partner selection, and policy recommendations (e.g., simplifying P2P regulations; enabling P2P-traded solar to count toward DISCOM RPO).[3]
Partnerships with ISGF and DISCOMs were instrumental in validating technology and framing regulatory pathways. The company’s continued engagement contributed to regulatory changes in three states. AI-ECTA broadened openness to Australian solutions, increasing delegations and collaborations and improving receptivity among Indian utilities and regulators. Memberships and partnerships (e.g., UN energy compact, Smart Energy Council, 24/7 CFE, EnergyTag) bolstered credibility on time-stamped energy attributes and 24/7 matching practices.
Strategic bets and sequencing
- Bet on proof before scale: Establish viability of P2P trading in India’s complex market via pilots while actively shaping regulatory understanding.
- Build for scale early: Integrate a high throughput blockchain (Solana) to handle future commercial transaction volumes even as pilots run amid hardware constraints.
- Policy-through-evidence: Use pilot results and KPIs to advocate simplification of P2P regulations, standardised metering, smart meter penetration, billing integration, and formal recognition of P2P-traded solar for DISCOM RPO.[4]
"Powerledger entered the Indian market in 2018, selecting Uttar Pradesh as the initial state for deployment. The key driver for choosing India was the country’s rapid and ambitious energy transition.

Impact & Results
Powerledger’s India pilots demonstrated that blockchain-enabled P2P trading can function across varied regulatory and infrastructure contexts, strengthening the company’s position as a trusted innovator in decentralised energy markets. The pilots highlighted the benefits of local matching, real-time settlement, and transparent provenance, laying a foundation for granular REC markets and 24/7 CFE procurement using time-stamped certificates.
The early India strategy prioritised demonstration over immediate revenue, but the disciplined KPI framework, participant counts, traded energy volumes, enrolled renewable capacity, and indicative savings sharpened product-market fit, partner prioritisation, and commercialisation planning. The evidence base increased interest from utilities and large corporates seeking precise decarbonisation alignment and auditability, improving medium-term pipeline quality.
Sustained engagement contributed to regulatory changes in three states, an important indicator of policy movement toward commercial enablement. Pilots, workshops, and whitepapers supported capacity building across utilities and regulators, improving ecosystem readiness for decentralised trading and blockchain-based settlement.
Powerledger’s granular tracking and visualisation support robust ESG reporting and 24/7 matching frameworks. Integration with Solana positions the platform for mass transaction handling, a critical capability for future commercial rollouts. India’s role as a testbed creates a replicable template for other emerging markets facing similar constraints in metering, regulatory evolution, and rooftop solar utilisation.
What to measure going forward
- Pilot-to-policy conversion (number and depth of regulatory changes influenced)
- Hardware readiness within target cohorts (smart meter and standardised solar metering penetration)
- Pilot conversion to commercial contracts (including billing integration milestones)
- Enterprise adoption of time-stamped certificates and 24/7 matching as part of ESG programs.
A main obstacle to scaling operations was the absence of a regulatory framework enabling P2P energy trading on a commercial scale. Powerledger’s deep engagements and successful projects laid the groundwork for regulatory changes in three states.
Lessons & Insights
Market Entry & Strategy
Built trust with DISCOMs and regulators through education, transparent pilots, and clear communication of benefits in terms of grid reliability, regulatory alignment, and consumer value.
Adopted a state-by-state localisation model rather than a uniform national approach, recognising India’s fragmented power landscape.
Core Takeaway
In complex infrastructure markets, credibility and trust-building must precede scale.
Regulatory & Policy Environment
Lack of clear commercial frameworks for P2P energy trading slowed progress; pilots moved forward without billing integration but highlighted the need for regulatory clarity.
Advocacy centred on automated settlement, standardised metering, and recognition of P2P-traded solar toward DISCOM Renewable Purchase Obligations (RPOs).
Core Takeaway
Policy engagement and regulatory design are as important as technology in unlocking commercial viability.
Operational & Technical Constraints
Limited adoption of smart meters, challenges in metering shared rooftops, and tariff diversity complicated implementation.
Successful commercialisation requires synchronised readiness: policy, hardware, and billing systems must align simultaneously.
Core Takeaway
Technology-led pilots succeed only when infrastructure readiness matches innovation.
Organisational & Capability Building
Developed blockchain systems capable of handling commercial-scale transaction volumes.
Institutionalised KPI-driven partner selection to prioritise geographies and cohorts with higher infrastructure maturity.
Core Takeaway
Scalability requires not just tech readiness but disciplined partner and geography selection.
Broader Lessons for Cross-Border Business
Aligning incentives with local utilities especially around payment collection and revenue-sharing proved critical to overcoming institutional resistance.
Long-term public–private engagement was necessary to bridge gaps between global technology standards and local policy frameworks.
Core Takeaway
Success in emerging markets comes from aligning innovation with incumbent incentives and regulatory priorities.
All information has been verified from primary company submissions, official filings, interview transcripts, and secondary materials cited in the References section.
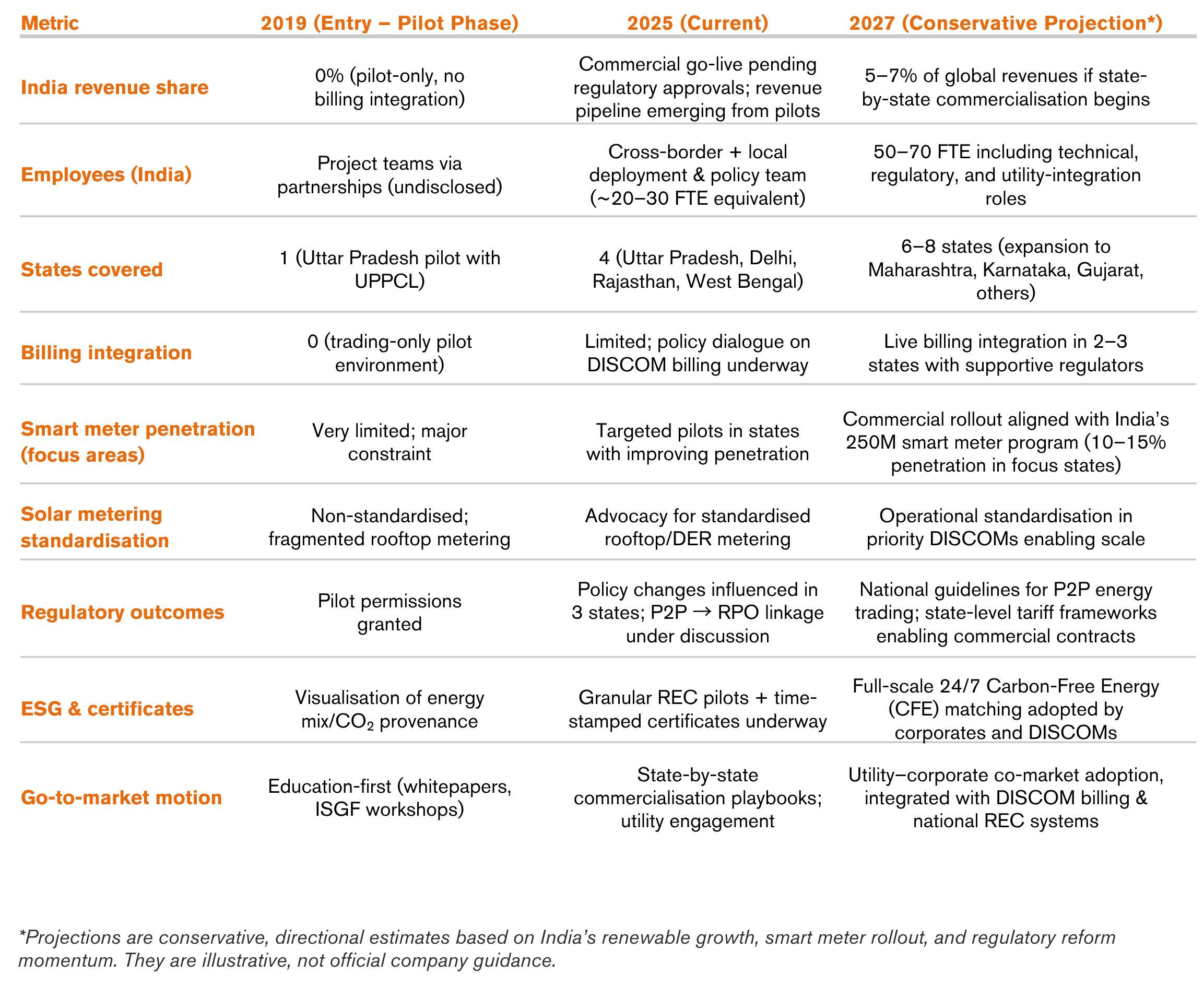
Company Snapshot

KPI Impact Snapshot