"We set up the first of its kind state-of-the-art third-party flexible endoscope repairs workshop in Hyderabad, India"
Context & Opportunity
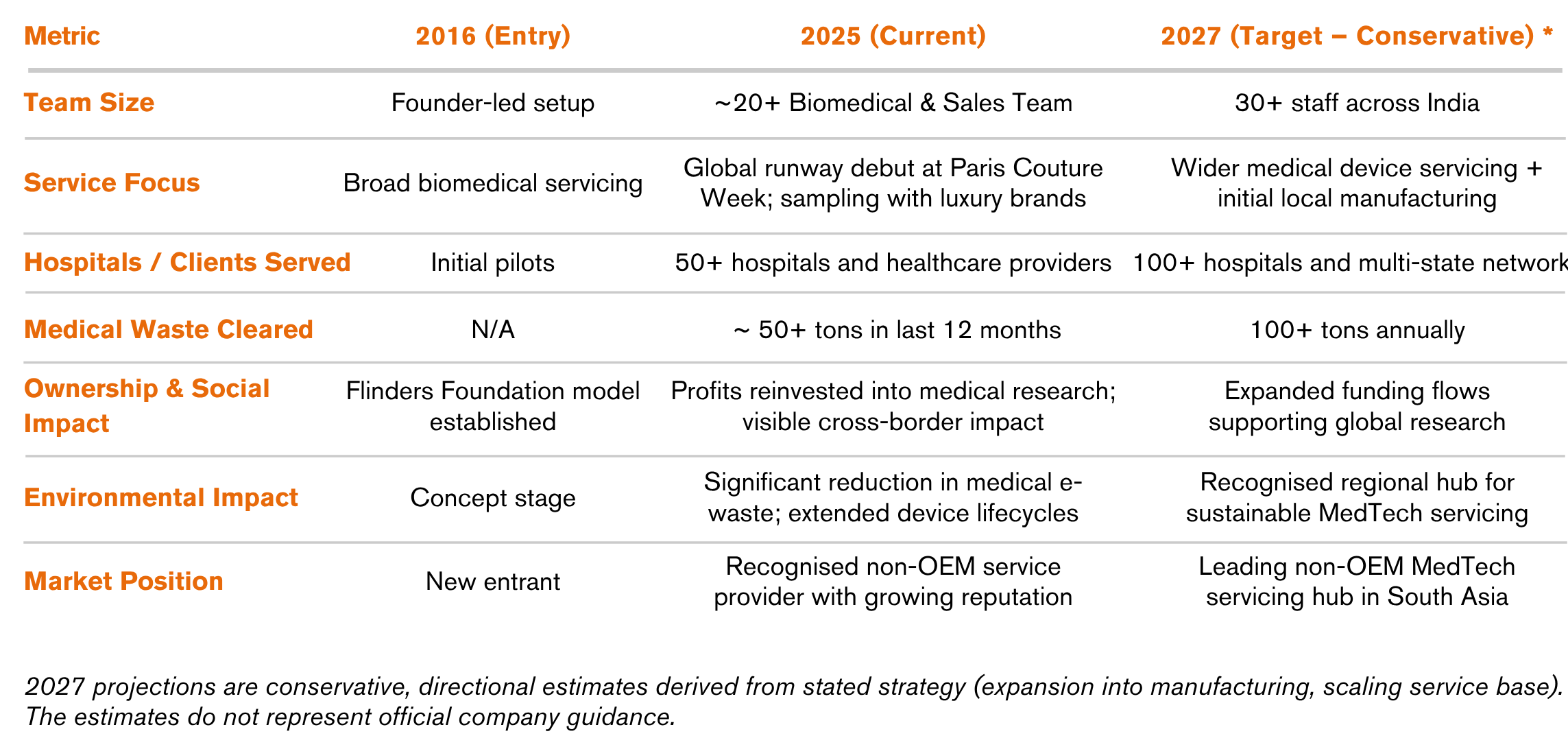
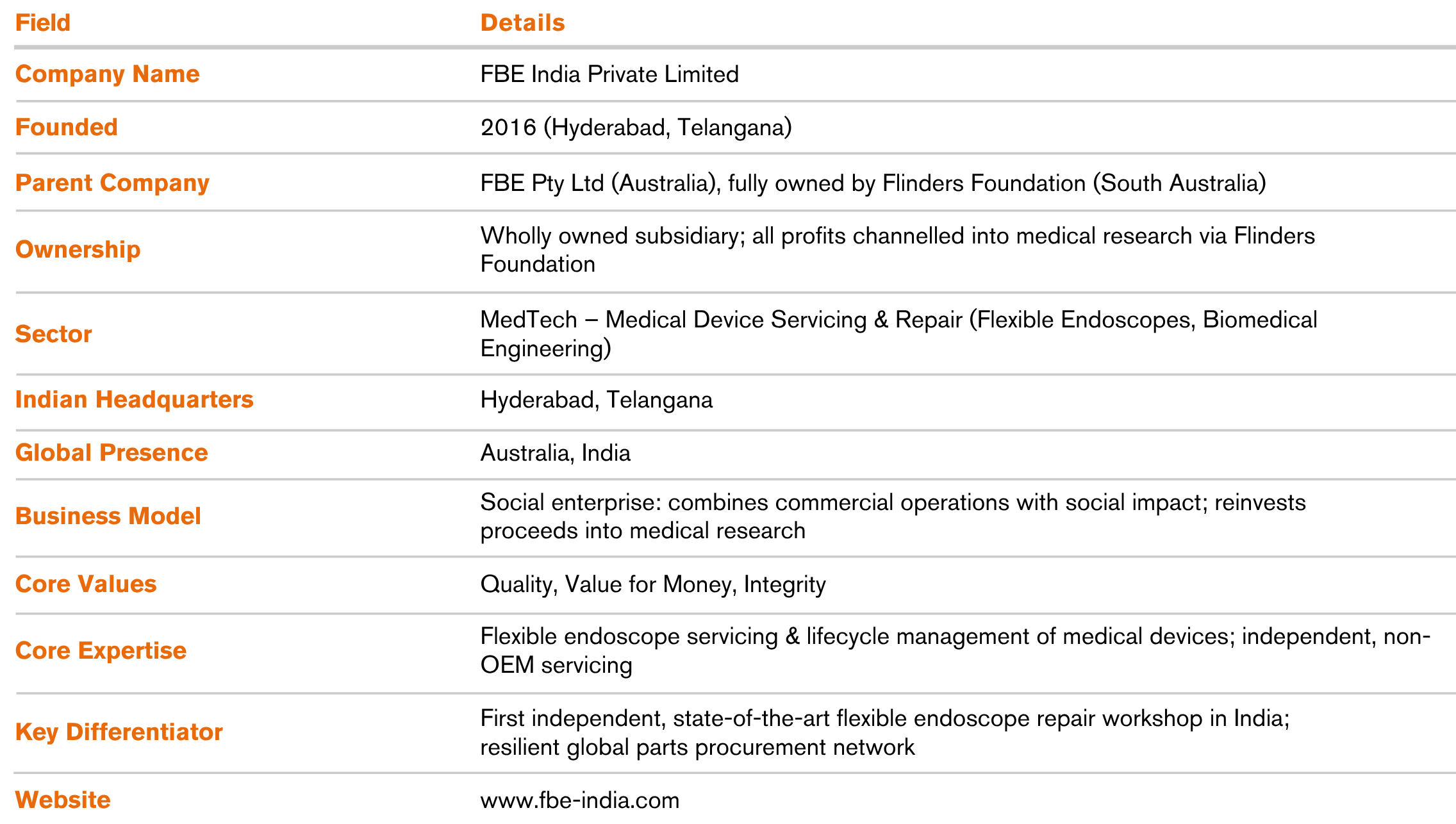
FBE India Private Limited was incorporated in October 2016 in Hyderabad, Telangana, marking the formal entry of a specialist Australian firm into the expanding Indian healthcare market. It was established as a private, wholly owned subsidiary of its Australian parent, FBE Pty Ltd. This ownership structure is central to the company’s identity and mission. The parent entity, Flinders Biomedical Enterprises (FBE) Pty Ltd, is fully owned by the Flinders Foundation, the official fundraising arm of the Flinders Medical Centre and Flinders University in South Australia.[1] This creates a unique business model where commercial success is directly linked to social impact; all business proceeds generated by FBE India are channelled back into medical research through the foundation. This structure frames FBE India not as a conventional multinational corporation driven solely by shareholder returns, but as a social enterprise operating with a dual mandate. Its leadership philosophy is anchored in the core values of quality, value for money, and integrity principles that guide its operational and strategic decisions.
FBE’s entry into India coincided with a period of significant transformation in the country's healthcare sector. In 2016, the overall Indian health care market was valued at approximately US$110 billion and was experiencing rapid expansion, driven by rising costs, increased health awareness, and growing burden of lifestyle diseases.[2] Medical devices, recognised as a ‘sunrise sector’ under India’s 2014 Make in India campaign, became a policy focus for domestic manufacturing and innovation. Yet the industry’s growth remained constrained by a critical structural weakness, heavy dependence on imports
FBE India entered with a broad mandate to deliver biomedical engineering lifecycle management for large hospitals. Early market engagement, however, revealed an acute gap in flexible endoscope servicing, a high-cost, underserved niche. OEMs exacerbated the problem by imposing prohibitive repair charges and withdrawing support for older devices under planned obsolescence practices. With Cost-of-Service Ratios (COSR) reaching 20–25%, hospitals often spent the device’s full purchase price on maintenance within four to five years. This structural inefficiency created a clear opening for independent providers, who could deliver 20–70% cost savings versus OEMs. Recognising this was the strategic inflection point that drove FBE’s pivot to flexible endoscope repair as its core focus.

Strategy & Execution
FBE entered India through a greenfield investment, establishing a wholly owned subsidiary to retain full control over operations, quality, and strategic direction. The entry strategy, designed in-house, reflected a lean and self-reliant approach, anchored by a deliberate localisation choice: Hyderabad as the hub, selected for its logistics connectivity across South and Central India. Pricing was adapted to Indian market cost structures, reinforcing commercial relevance.
The most immediate barrier was OEMs’ refusal to supply spare parts, an entrenched anti-competitive practice. FBE responded by building a resilient international procurement network spanning the US, Europe, and Australia. What began as a vulnerability became a core competency, positioning FBE at the forefront of the global ‘Right to Repair’ movement.
Initially reliant on a centralised network of exclusive channel partners, the model faltered under COVID lockdowns. FBE pivoted quickly, shifting to a non-exclusive, regionally distributed partnership model. This move created a decentralised, more resilient sales and service network, a strategic agility that proved vital to survival and positioned the company for scalable growth.
"OEMs were not welcome to see a third-party repair/service company foraying into the market. As a result, we had to procure parts from the USA, Europe or Australia.
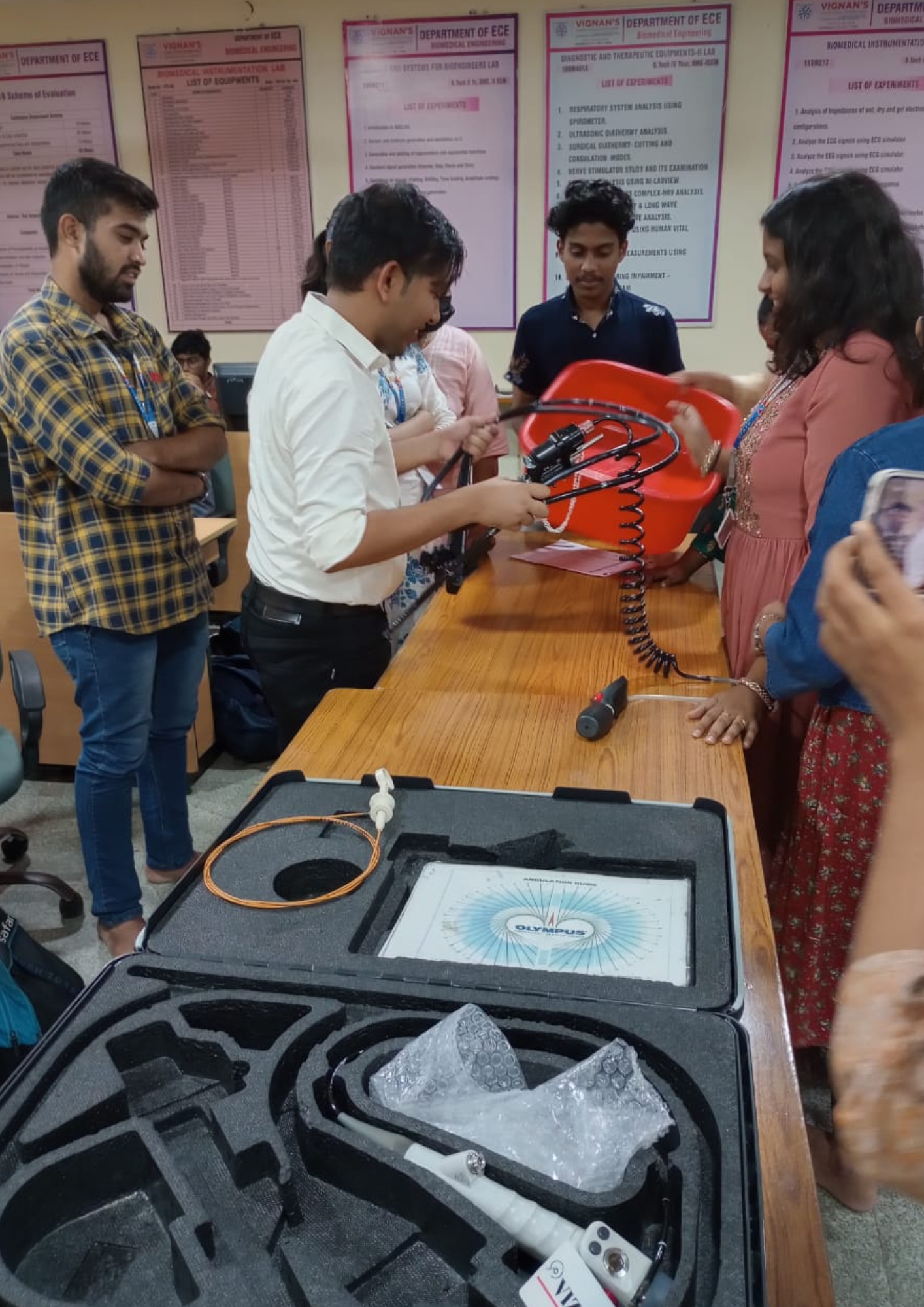

Impact & Results
Since inception, FBE India has delivered multi-dimensional impact, validated the strength of its disruptive service-led model and established the foundation for future expansion into manufacturing and after-sales support.
Impact has extended well beyond financial performance. The company’s unique ownership structure, profits reinvested into medical research through the Flinders Foundation embeds social value directly into its operating model. Environmentally, FBE has already diverted 37 tons of medical device waste from landfills, a meaningful contribution in a country ranked as the world’s third-largest e-waste producer.
This dual focus on sustainability and social good creates a self-reinforcing value chain across the Australia–India corridor: Indian hospitals benefit from lower-cost, higher-quality servicing; the resulting profits are channelled back into global medical research; and those innovations cycle back to improve healthcare systems, including India’s.
Strategically, FBE India has positioned itself not just as a service provider but as a future regional hub. By laying the groundwork for manufacturing and expanded device support, the company is transitioning from niche disruptor to an integrated MedTech platform aligned with India’s long-term industrial and healthcare priorities.
"Quality, Value for Money & Integrity are our core values. FBE India is owned by FBE Pty, which is fully owned by Flinders Foundation. All the proceeds of business go into medical research.

Lessons & Insights
Market Entry & Strategy
Faced entrenched OEM resistance as incumbents withheld spare parts to preserve market control; FBE countered by building an independent global supply chain.
Pivoted during COVID-19 from an exclusive partner model to a non-exclusive network, ensuring scalability, resilience, and geographic reach.
Core Takeaway
In entrenched markets, resilience comes from anticipating incumbent pushback and adopting flexible, ecosystem-driven strategies.
Localisation & Ecosystem Building
Broadened channel partnerships to navigate India’s diversity, moving beyond rigid exclusivity to embrace local networks.
Embedded trust through alignment with community stakeholders and by tailoring operations to India’s scale and complexity.
Core Takeaway
In India’s vast, heterogeneous market, open ecosystems and distributed partnerships outperform narrow, exclusive arrangements.
Organisation & Cross-Cultural Alignment
Established non-negotiable principles, Quality, Value for Money, Integrity while remaining flexible in day-to-day interactions with Indian partners.
Built credibility by blending global standards with local adaptability, ensuring trust and long-term relationships.
Core Takeaway
Cross-cultural success requires protecting core values while adapting practices to local norms and expectations.
Broader Lesson for Cross-Border Business
Positioned to evolve from service-led operations to local manufacturing, aligning with India’s ‘Make in India’ and National Medical Device Policy 2023, which targets a USD 50B market by 2030.
Demonstrated that embedding in national industrial priorities strengthens long-term legitimacy and growth potential.
Core Takeaway
Long-term success in India comes from aligning business strategy with national policy priorities and embedding in local ecosystems.

All information has been verified from primary company submissions, official filings, interview transcripts, and secondary materials cited in the References section.
Company Snapshot
KPI Impact Snapshot